Austria: Large-Scale Solar Plants Subsidy Scheme Shows Increase in Average System Sizes
January 3, 2014
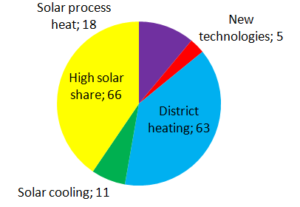
2013 was already the fourth year for the Austrian Climate and Energy Fund’s subsidy scheme for large-scale solar systems.The demand for it was also still great: All in all, 37 projects profited from a total subsidy amount of about EUR 4.5 million (see the attached document). 18 of these projects were accompanied by case studies. The programme subsidises large-scale solar plants across the following application areas: solar process heat (6 systems), solar feed-ins into heat networks (11 systems), high solar coverage (15 systems), solar-supported air conditioning in combination with warm water and heating (4 systems), as well as new technologies and innovative approaches (1 system). The pie chart shows the shares of the aforementioned applications in the total subsidised collector area.
In 2013, the Austrian Climate and Energy Fund provided financial support to a total of 37 large-scale solar plants. With 1.6 million, the biggest chunk of the subsidy amount went to the six projects in the Solar Process Heat category. The subsidised systems amount to a combined 5,332 m² of collector area, which corresponds to a share of 36% in the total subsidised area (see figure). With an average collector area of 889 m², these plants are the largest (see the following table). The second biggest piece of the subsidy budget was granted to the 15 systems with high solar coverage. The plants with a collector area of altogether 3,401 m² (23%) were subsidised with more than EUR 1 million. The 11 systems which feed the generated heat into the heat network had one more percentage point (24%), adding up to 3,552 m² of collector area.These projects were subsidised with, all in all, EUR 857,130.
| Application area |
No. of |
Collector |
Average |
Total Subsidy |
| High solar coverage |
15 |
3,401 |
227 |
1,089,686 |
| District heating |
11 |
3,523 |
320 |
857,130 |
| Process heat |
6 |
5,332 |
889 |
1,643,149 |
| Air conditioning |
4 |
2,318 |
579 |
639,831 |
| New technologies |
1 |
244 |
244 |
50,000 |
| Total |
37 |
14,818 |
400 |
4,279,796 |
2013’s 37 subsidised large-scale plants
Source: Klima- und Energiefonds
The Climate and Energy Fund’s programme had already been popular during the last three years: In 2010, it had supported 38 projects, while it had supplied grants to set up 52 systems in the following year. In 2012, it had helped finance 39 solar applications.
The total subsidised collector area has varied greatly throughout the years, starting at 18,404 m² in 2001 to 11,316 m² in 2012 and 14,817 m² in 2013. The 400 m² of average system size in 2013 is much higher than in the years before (290 m² in 2012 and 354 m² in 2011). The following table about systems subsidised in 2011 and 2012 makes apparent some of the trends in recent years. The number of district heating systems has been decreasing year after year, from 27 in 2011 to 11 in 2013. On the other hand, there has been an increase in the average size of the process heat plants over the years, from 262 m² in 2011 to 889 m² per system in 2013. The High Solar Coverage category with an average plant size of 200 m² shows a constantly high number of systems (between 13 and 15). The New Technology category is a 2013 addition, which has only one system to show for at the moment.
|
Application |
Total |
No. of |
Average |
Total |
No. of |
Average |
| Solar cooling |
3,683 |
7 |
526 |
863 |
4 |
216 |
| High solar coverage |
3,357 |
15 |
224 |
2,167 |
13 |
167 |
| District heating |
10,577 |
27 |
392 |
3,786 |
14 |
270 |
| Process heat |
787 |
3 |
262 |
4,500 |
8 |
563 |
| Total |
18,404 |
52 |
354 |
11,316 |
39 |
290 |
Projects subsidised in 2011 and 2012
Source: Climate and Energy Fund
Source: Climate and Energy Fund
More information: